

JSF 2 example to delete row in dataTable.
#Jsf with icefaces update
JSF 2 example to update row in dataTable.

JSF 2, and tags to display data in a HTML table format. example, set a value directly into the property of your backing bean.Īdd, update, delete and sorting data in via JSF’s dataTable. JSF 2 setPropertyActionListener example.example, pass a attribute to a component. example, pass a parameter to a component. JSF 2 link, commandLink and outputLink example.JSF 2 multiple select dropdown box example.

JSF 2.0 Internationalization or multiple language example. For maintainability concern, it’s recommended to put all the messages in the properties file, instead of hard-code the message in the page directly. In this tutorial, we show you the use of resource bundle to display the messages in the JSF 2.0. JSF’s message manipulation and Internationalization. See following example to differentiate between the page forward and page redirect. In this case, you can use “ form-action” element to differentiate the two navigation cases.īy default, JSF performs a server page forward while navigating to another page. In JSF navigation rule, you may encounter a situation where two separate actions return a same “ outcome” in a page. JSF “form-action” navigation rule example.JSF 2 comes with a very flexible conditional navigation rule to solve the complex page navigation flow. Now, JSF 2 come out a new “auto view page resolver” mechanism named “implicit navigation“, where you don’t need to declare the above navigation rule, instead, just put the “view name” in the action attribute and JSF will find the correct “view page” automatically. In JSF 2.0, a new annotation is used to dependency injection (DI) a managed bean into the property of another managed bean. The managed bean can be a normal Java bean, which contains the getter and setter methods, business logic or even a backing bean (a bean contains all the HTML form value). In JSF 2.0, Java bean that can be accessed from JSF page is called Managed Bean. Later, you can reference this “library” with JSF tag’s library attribute.Ībout managed bean configuration and injection in JSF 2.0 In JSF 2.0 terminology, all the sub-folder name of the “resources” folder is considered as a “library” in JSF 2.0 web application. In JSF 2.0, all your resources files like css, images or JavaScript, should put into a “resources” folder in the root of your web application.
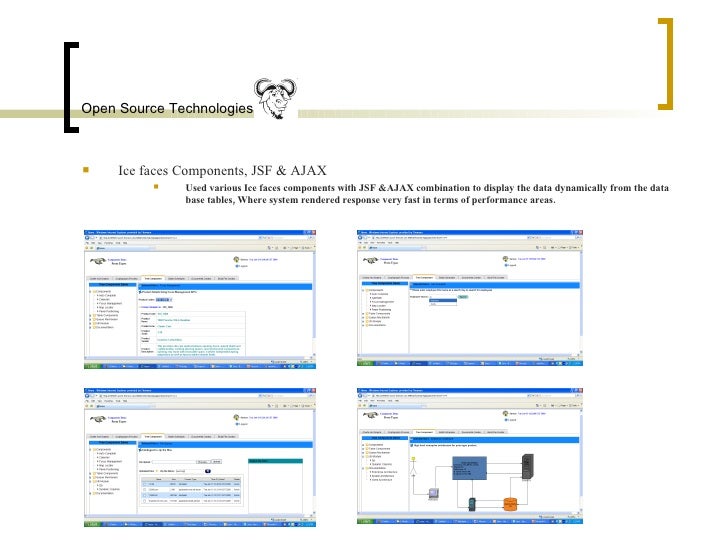
#Jsf with icefaces how to
Here’s a quick guide to show how to enable the JSF 2.0 features in Eclipse projects.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
